Basic Information
Secondary Structure
Secondary Structure
Secondary structure that contributes a minimum of free energy.
Thermodynamic properties of the Boltzmann ensemble.
Structure Prediction
Transcripts
| ID | Sequence | Length | GC Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| NM_001286356.2 | AGACCAGACCAACAGUAACACCAAGGGCAGGUGGGCAGGCCUCCGCCCU… | 724 nt | 0.5787 |
| NM_001286357.2 | AGACCAGACCAACAGUAACACCAAGGGCAGGUGGGCAGGCCUCCGCCCU… | 605 nt | 0.5818 |
| NM_001286358.2 | AGACCAGACCAACAGUAACACCAAGGGCAGGUGGGCAGGCCUCCGCCCU… | 673 nt | 0.5825 |
| NM_001286359.2 | AGACCAGACCAACAGUAACACCAAGGGCAGGUGGGCAGGCCUCCGCCCU… | 727 nt | 0.5928 |
| NM_002762.4 | AGACCAGACCAACAGUAACACCAAGGGCAGGUGGGCAGGCCUCCGCCCU… | 680 nt | 0.5838 |
Summary
Protamines substitute for histones in the chromatin of sperm during the haploid phase of spermatogenesis, and are the major DNA-binding proteins in the nucleus of sperm in many vertebrates. They package the sperm DNA into a highly condensed complex in a volume less than 5% of a somatic cell nucleus. Many mammalian species have only one protamine (protamine 1); however, a few species, including human and mouse, have two. This gene encodes protamine 2, which is cleaved to give rise to a family of protamine 2 peptides. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have also been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]
Forensic Context
No forensic context available.
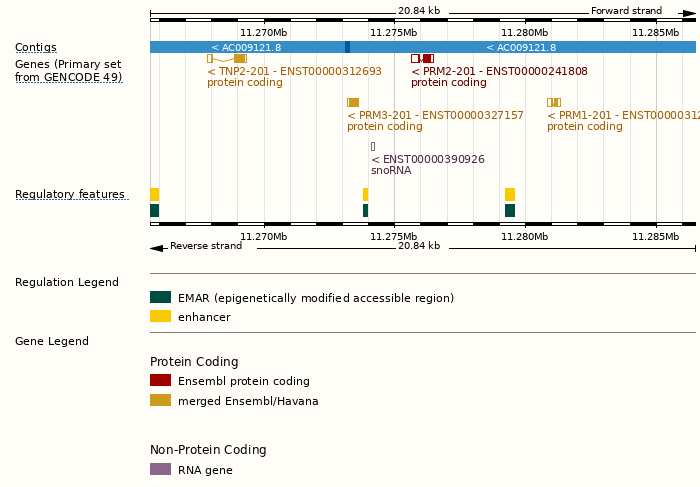
Genomic Tracks